The rapid growth of biotechnology drove the maturation of both cell therapy and gene therapy. Cell therapy, categorized according to the type of cells used for treatment, includes both stem cell therapies and immune cell therapy, such as CAR-T, TCR-T, and CAR-NK. The most significant of these varieties is CAR-T therapy.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell therapy, known as CAR-T cell therapy, is a novel technique that utilizes adoptive immunotherapy to treat tumors. CAR is composed of three structural components: an extracellular antigen-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain. Compared to conventional immunization therapies, CAR-T cells have both superior specificity and longer-lasting efficacy. These cells can recognize and target tumor antigens, demonstrating remarkable success in treating malignant tumors, particularly hematomas, and can destroy tumor cells without antigen presentation.
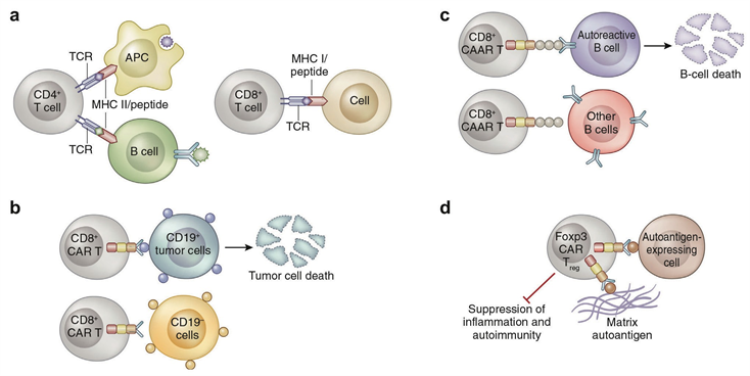
Application of CAR-T cell therapy in immune-related diseases[1].
Advantages:
The NCG mouse, a severely immunodeficient strain produced and established independently by GemPharmatech, is obtained by utilizing gene editing technologies to knock out the Prkdc and Il2rg genes of the NOD/ShiltJGpt mice. This mouse is fully devoid of T-cells, B-cells, and NK cells, and is ideal for evaluating the efficacy and safety of CAR-T therapy and related cell therapies due to its status as the most immunodeficient mouse model.
GemPharmatech has established CDX and PDX libraries with independent property rights, including a range of solid tumors and hematological system tumors, and offering an abundance of services using these tumor model resources for CAR-T therapy effectiveness research. We additionally possess a mouse in vivo imaging system, which is utilized to detect various mouse tumor models and metastatic tumor models in situ. Similarly, GemPharmatech has also developed techniques for absolute CAR-T cell counting and cytokine detection in peripheral blood, which addresses CAR-T investigations’ testing requirements.

Applications of in vivo imaging system: observation of tumor burden after in situ xenograft of hematomas and solid tumors (encephalic glioma, hepatic carcinoma, etc.), determination of tumor growth, and efficacy evaluation for test antitumor drugs.
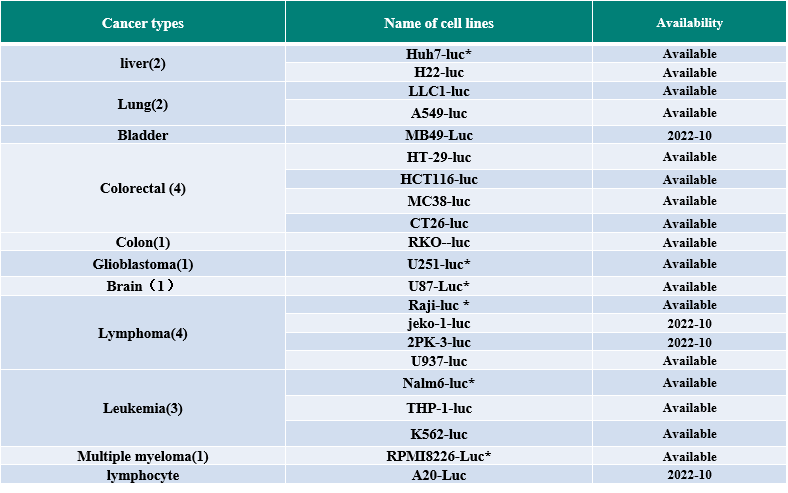
*:Tumorigenicity test
Service Specifications:
1. In vivo efficacy test on CDX (Nalm6-Luciferase) models
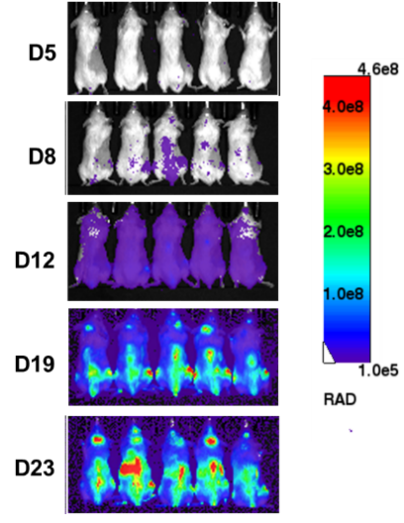
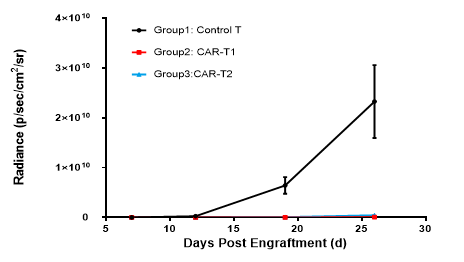
After tail vein inoculation of NCG mice with Nalm6-Luciferase cells, tumor load was detected using in vivo imaging on day 5, 8, 12, 19, and 23. The progression of tumor load in mice can be determined based on the signal intensity of in vivo imaging.
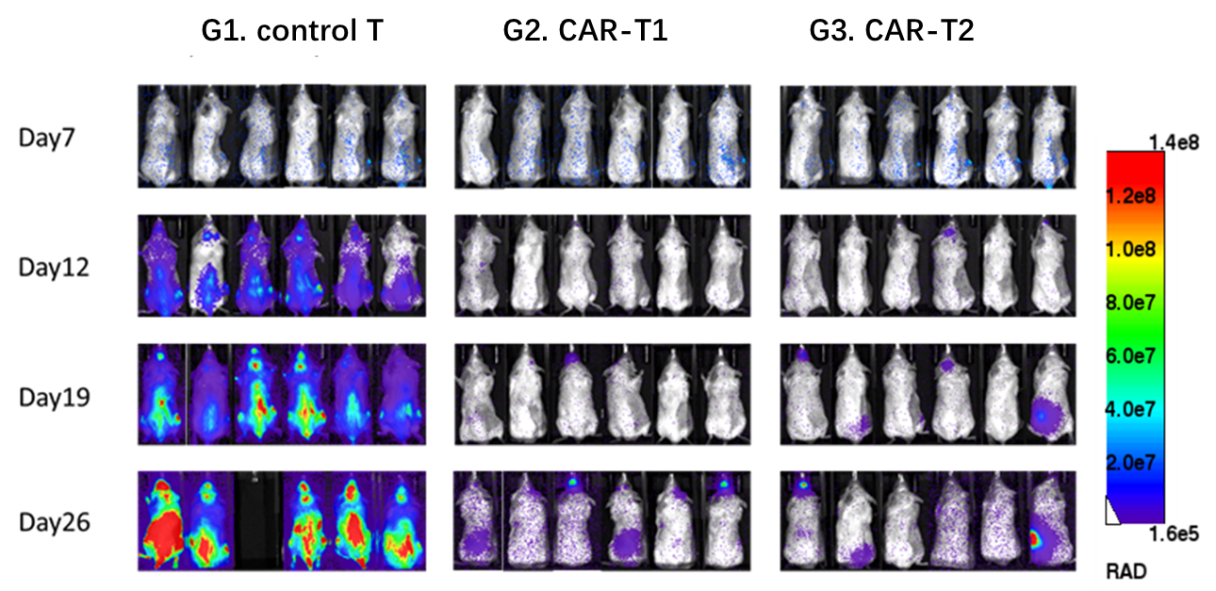
Collaboration data with 3rd party
The NCG mice were inoculated intravenously with Nalm6-Luciferase cells. After 7 days, the mice were randomly allocated into three groups. Then the mice were treated with control T, CAR-T1 and CAR-T2.
CAR-T1 and CAR-T2 had obvious inhibitory effects on tumor growth (TGI, CAR-T1=100.00%, TGI, CAR-T2=100.00%), indicating NCG mice as the ideal animal model to evaluate the efficacy of CAR-T.
References
[1] Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR T) cells: another cancer therapy with potential applications in kidney disease and transplantation? Kidney Int., 2018, 94(1): 4-6.

