Because BALB/c mice are more susceptible to immune-related adverse events (irAEs), GemPharmatech provides immune-checkpoint inhibitor-related toxicity evaluations. The irAEs of immune-checkpoint inhibitors can be evaluated by clinical observation of mice, pathological evaluation, testing of cytokines, and monitoring of clinical indexes dynamically during the dosing process, all of which provides an effective toxicity evaluation platform for preclinical research of ICIs.
BALB/c-hCTLA4 Models
The toxic side effects of anti-PD1 + anti-CTLA4 combination therapy were evaluated with C57BL/6-hPD1/hCTLA4 and BALB/c-hPD1/hCTLA4 mice, respectively.
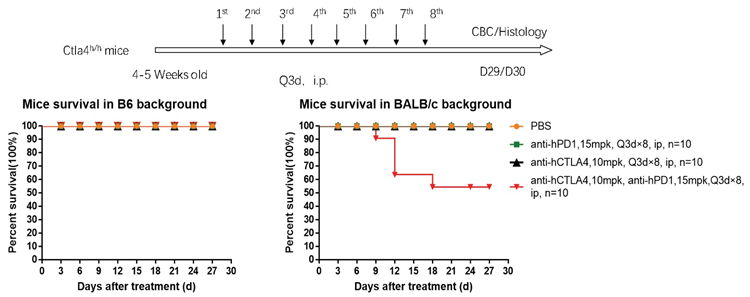
1. The survival curve of the PD1 antibody + Yervoy combo therapy in B6 and BALB/c mice showed that BALB/c mice died on Day 9 and were not tolerant until Day 18 in the study.
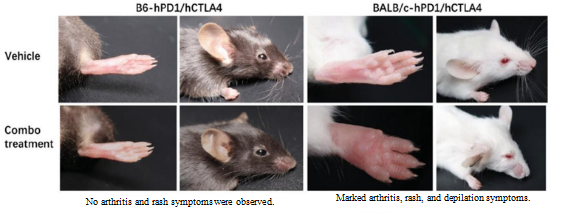
2. Clinical trial data for the CTLA4-targeting drug Yervoy showed that patients suffered severe side effects, including dermatitis, hepatitis, diarrhea, and rectocolitis. BALB/c mice exhibited pathological symptoms such as arthritis, rashes, and depilation, but B6 mice exhibited no such symptoms.

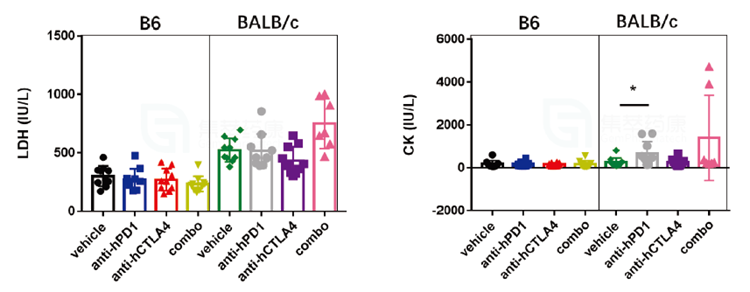
3. During the clinical biochemical assessment of Yervoy, the levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and creatine kinase (CK) were significantly higher in BALB/c mice than in B6 mice, indicating that the cardiac damage produced by Yervoy was more severe in BALB/c animals.
4. Yervoy caused inflammatory injury on mice hearts to varied severity. Inflammatory lesions observed in BALB/c murine hearts were more severe than in B6 background mice.
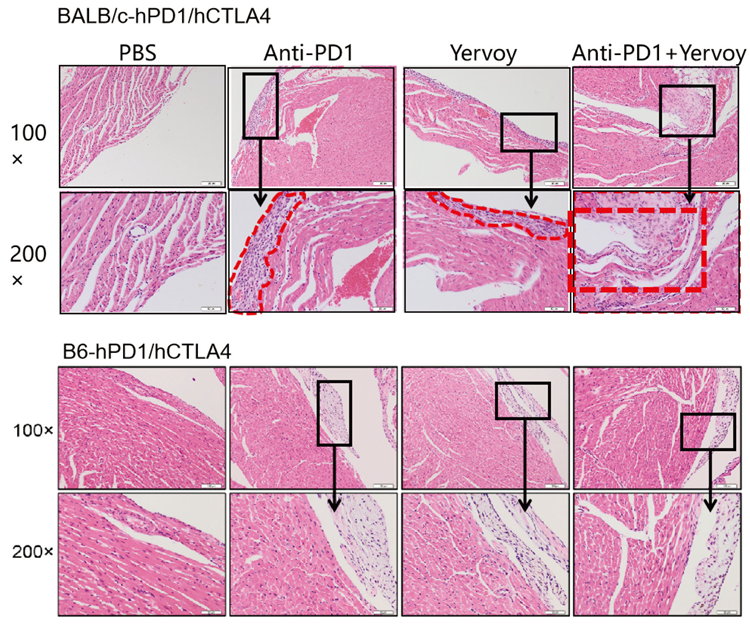
B6-hPD1/CTLA4 mouse models proved tolerant to drug therapies; humanized immune checkpoint BALB/c-hPD1/hPD1 mice make ideal models for evaluating macromolecular and small-molecule drug toxicity in preclinical trials due to their ability to reproduce certain adverse reactions (ARs) in clinical practice.

